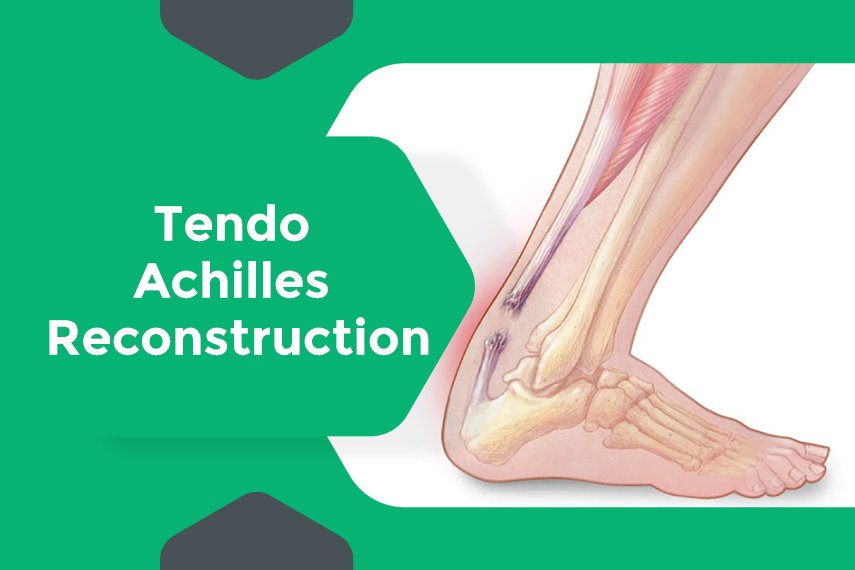
Tendo Achilles reconstruction

Amputation is considered when a severe infection does not respond to other treatments and poses a risk to the patient's life. It aims to prevent the spread of infection and save the patient's life.
Recovery involves wound care, physical therapy, and rehabilitation to adapt to the loss of the limb. Patients may also receive prosthetics to aid in mobility. The recovery time can vary depending on the patient's overall health and the extent of the amputation.
Risks include infection, blood clots, and complications related to anesthesia. However, amputation is performed to save the patient's life and prevent the spread of a life-threatening infection.
To amputate means to surgically remove a limb or part of a limb, such as an arm, leg, foot, hand, toe, or finger, usually because of injury, infection, or disease.
The process involves administering anesthesia, making an incision to remove the damaged tissue, controlling bleeding, and shaping the remaining limb for prosthetic fitting. The wound is then closed and dressed.
An amputated leg is referred to as a residual limb or stump.
Types of amputations include partial foot amputation, below-knee amputation, above-knee amputation, and disarticulation (removal of a joint).
The pain from losing a limb varies. While the surgery is performed under anesthesia, patients may experience post-operative pain and phantom limb pain, which can be managed with medication and therapy.
Doctors amputate to remove diseased, infected, or damaged tissue that cannot heal, to prevent the spread of infection, and to save the patient's life.
Amputations are done by administering anesthesia, making an incision to remove the affected limb, controlling bleeding, and shaping the residual limb. The wound is then closed with sutures.
The two main types are major amputations (removal of part or all of a limb) and minor amputations (removal of fingers or toes).
A ghost limb, or phantom limb, is the sensation that an amputated or missing limb is still attached. Patients may feel pain or other sensations as though the limb is still there.
Amputation is considered when a severe infection does not respond to other treatments and poses a risk to the patient's life. It aims to prevent the spread of infection and save the patient's life.
Recovery involves wound care, physical therapy, and rehabilitation to adapt to the loss of the limb. Patients may also receive prosthetics to aid in mobility. The recovery time can vary depending on the patient's overall health and the extent of the amputation.
Risks include infection, blood clots, and complications related to anesthesia. However, amputation is performed to save the patient's life and prevent the spread of a life-threatening infection.
Complications include infections, osteomyelitis, gangrene, and in severe cases, the need for amputation.
Book Your Appointment Today with Dr. Ashutosh Shah
Book Appointment© 2025. Surat Diabetic Foot And Ulcers Clinic. All Rights Reserved. Designed and developed by Trizone Healthcare